Introduction to Underactive Thyroid
An underactive thyroid, medically known as hypothyroidism, is a condition where the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient hormones. These hormones are crucial in regulating the body’s metabolism, and their deficiency can lead to a range of health issues. Recognizing the early indicators of an underactive thyroid is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve quality of life. This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and management strategies of hypothyroidism.
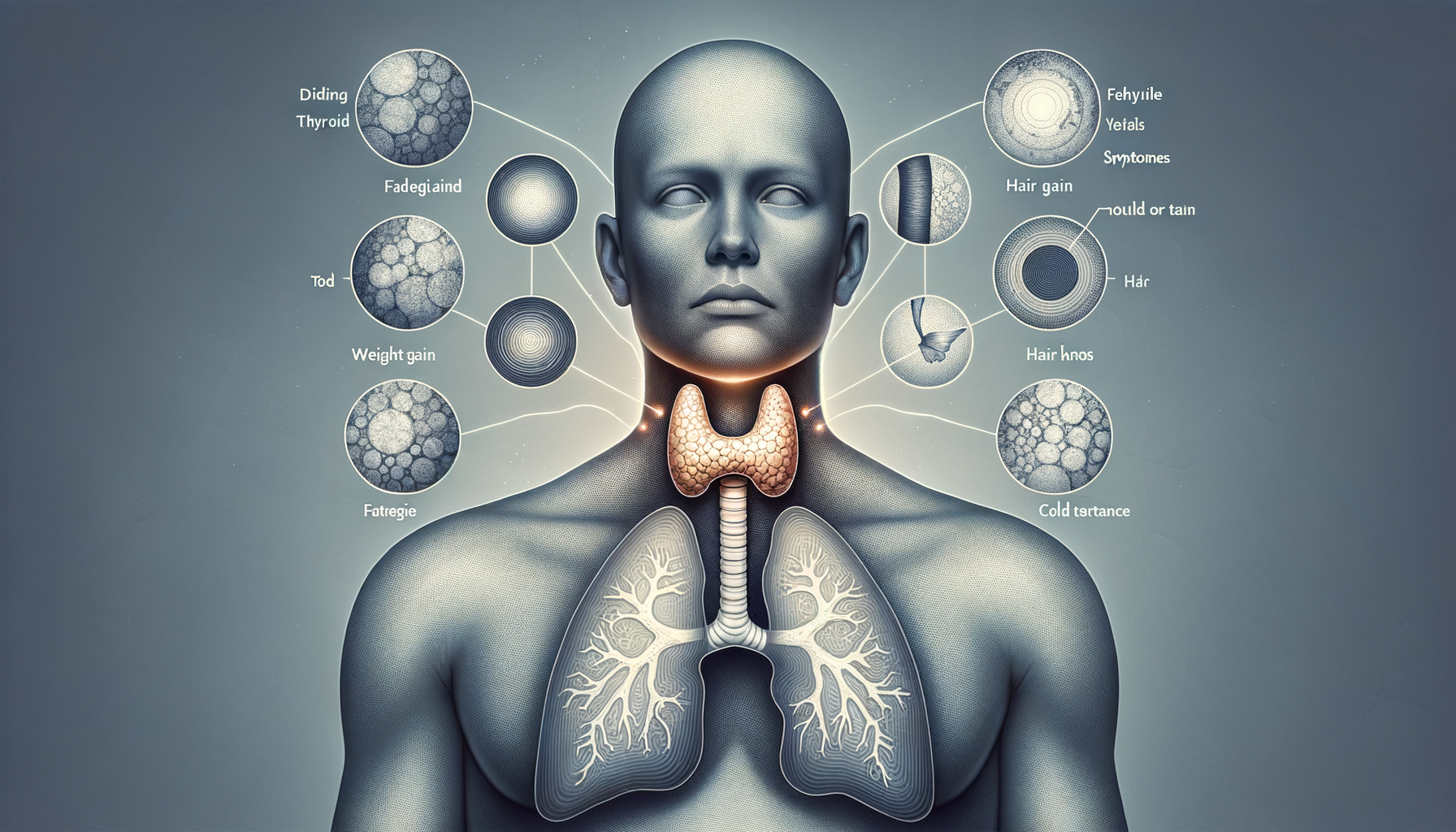
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
The symptoms of an underactive thyroid can vary widely among individuals, but some common signs often emerge. These include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight gain, and sensitivity to cold temperatures. Additionally, individuals may experience dry skin, hair loss, and muscle weakness. These symptoms can develop slowly, making them easy to overlook or attribute to other causes. Understanding these signs can prompt individuals to seek medical advice and testing, leading to early intervention.
Some other symptoms that might be observed include:
- Constipation
- Depression
- Memory problems
- Decreased heart rate
Recognizing these symptoms early can be challenging, but awareness is key to managing the condition effectively.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of hypothyroidism. The most common cause is an autoimmune disorder known as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. Other causes include iodine deficiency, certain medications, and treatments for hyperthyroidism. Risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing an underactive thyroid include being female, being over the age of 60, and having a family history of thyroid disease.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help in identifying individuals who might be at higher risk, allowing for proactive monitoring and management.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing hypothyroidism typically involves a series of blood tests that measure levels of thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). A high level of TSH and a low level of thyroid hormones indicate an underactive thyroid. In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to determine the underlying cause, such as testing for antibodies associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Early diagnosis is crucial as it allows for effective management of symptoms and prevention of complications. Regular screening is recommended for individuals with risk factors or those experiencing symptoms.
Management and Treatment Options
The primary treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones to restore normal levels. This treatment is usually lifelong, and regular monitoring is essential to ensure the correct dosage. In addition to medication, lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet rich in iodine and regular exercise can support thyroid health.
Managing hypothyroidism effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers to monitor hormone levels and adjust treatment as necessary.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Thyroid Health
Understanding the symptoms and causes of an underactive thyroid is the first step in managing this condition effectively. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life and prevent complications. By staying informed and proactive about thyroid health, individuals can take charge of their well-being and ensure that they receive the necessary care and support.



Leave a Reply