Introduction to Stroke Symptoms
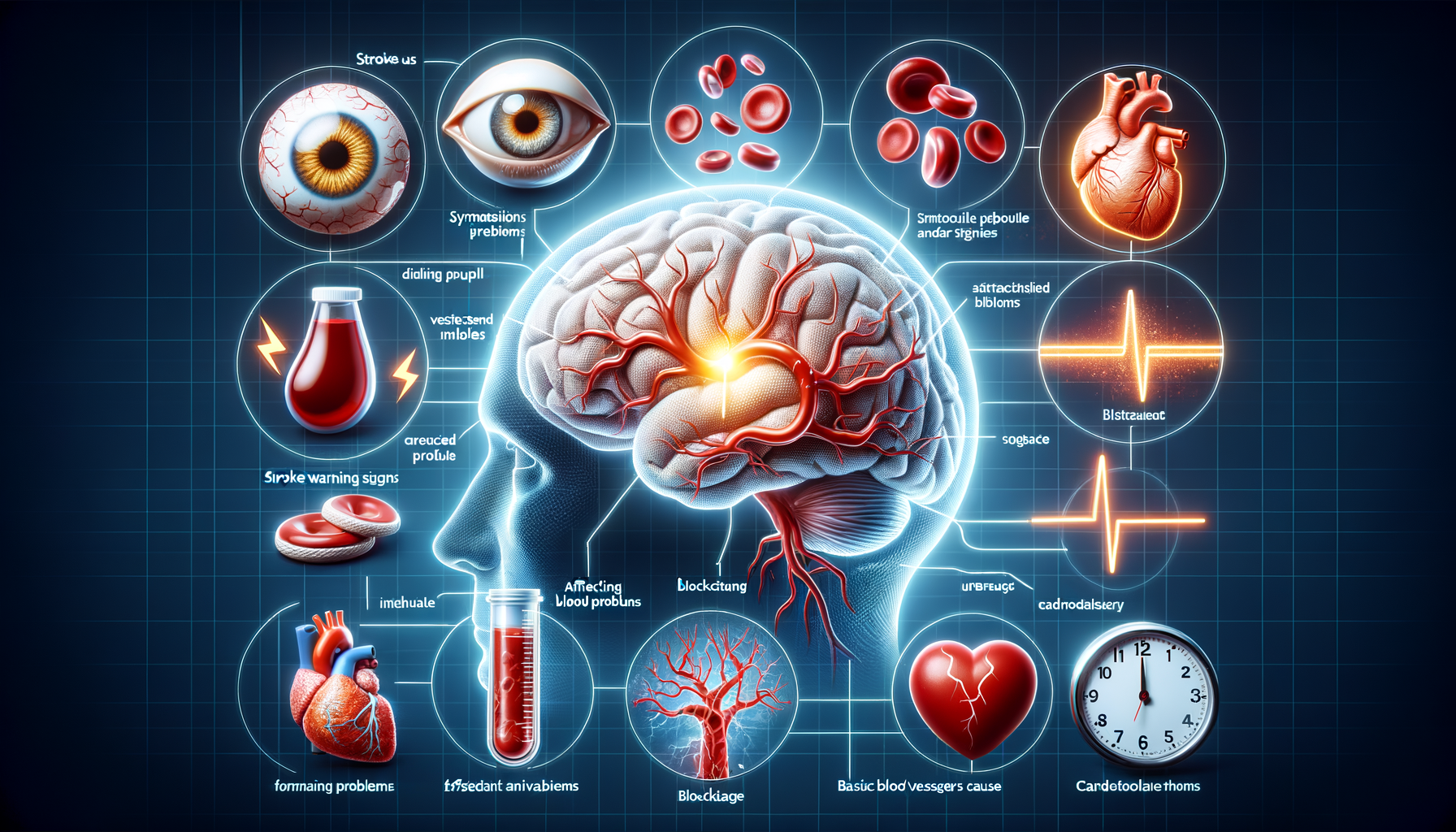
Understanding stroke symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention and can significantly impact recovery outcomes. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to brain cells dying within minutes, making it essential to act fast. Recognizing the signs of a stroke can be a lifesaver, not only for oneself but also for those around us.
Strokes are a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, affecting millions each year. Despite their prevalence, many people remain unaware of the symptoms and the urgency required in responding to them. This article delves into the warning signs of a stroke, the underlying causes, and the importance of immediate medical attention.
Common Symptoms of a Stroke
The symptoms of a stroke often appear suddenly and can vary depending on the part of the brain affected. The most common symptoms include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Difficulty walking, dizziness, loss of balance, or lack of coordination.
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity. Some individuals may experience all symptoms, while others may only have one or two. The key is the sudden onset of these symptoms, which differentiates a stroke from other medical conditions.
Types of Stroke and Their Causes
Strokes are broadly categorized into two main types: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes, accounting for about 87% of all cases, occur when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery leading to the brain. This can be caused by fatty deposits lining the vessel walls, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding in or around the brain. Common causes include high blood pressure, aneurysms, or trauma. Both types of strokes require immediate medical attention, but the treatments differ significantly.
Understanding the type of stroke is crucial for effective treatment. While ischemic strokes often require clot-busting drugs, hemorrhagic strokes might need surgical intervention to stop the bleeding and relieve pressure on the brain.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of a stroke, some of which are controllable, while others are not. Controllable risk factors include:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Obesity and physical inactivity
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Uncontrollable risk factors include age, gender, family history, and previous stroke or heart attack. However, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of stroke. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
Importance of Immediate Medical Attention
Time is of the essence when it comes to treating a stroke. The sooner a person receives medical treatment, the better the chances of recovery and reduced risk of long-term disability. The acronym F.A.S.T. is often used to help remember the signs of a stroke and the need for urgent action:
- Face drooping: Does one side of the face droop or is it numb?
- Arm weakness: Is one arm weak or numb?
- Speech difficulty: Is speech slurred or hard to understand?
- Time to call emergency services: If any of these symptoms are present, call emergency services immediately.
Quick response can make a significant difference in the outcome for stroke patients. Medical professionals can administer treatments that can minimize brain damage and improve recovery chances.
Conclusion: Recognizing and Responding to Stroke Symptoms
Recognizing the warning signs of a stroke and understanding the importance of immediate medical attention can save lives. With strokes being a leading cause of death and disability, awareness and education are vital. By knowing the symptoms and acting quickly, individuals can significantly impact their health outcomes and those of their loved ones.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors are key to prevention. However, should a stroke occur, the F.A.S.T. method serves as a crucial reminder of the need for urgent medical intervention. Stay informed, stay prepared, and act swiftly in the face of a stroke.



Leave a Reply