Introduction to Stroke Symptoms
Strokes are a medical emergency that require immediate attention. Recognizing the symptoms early can significantly improve the chances of recovery and reduce the risk of long-term disability. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. Understanding the warning signs and causes of strokes can empower individuals to act swiftly, potentially saving lives and improving outcomes.
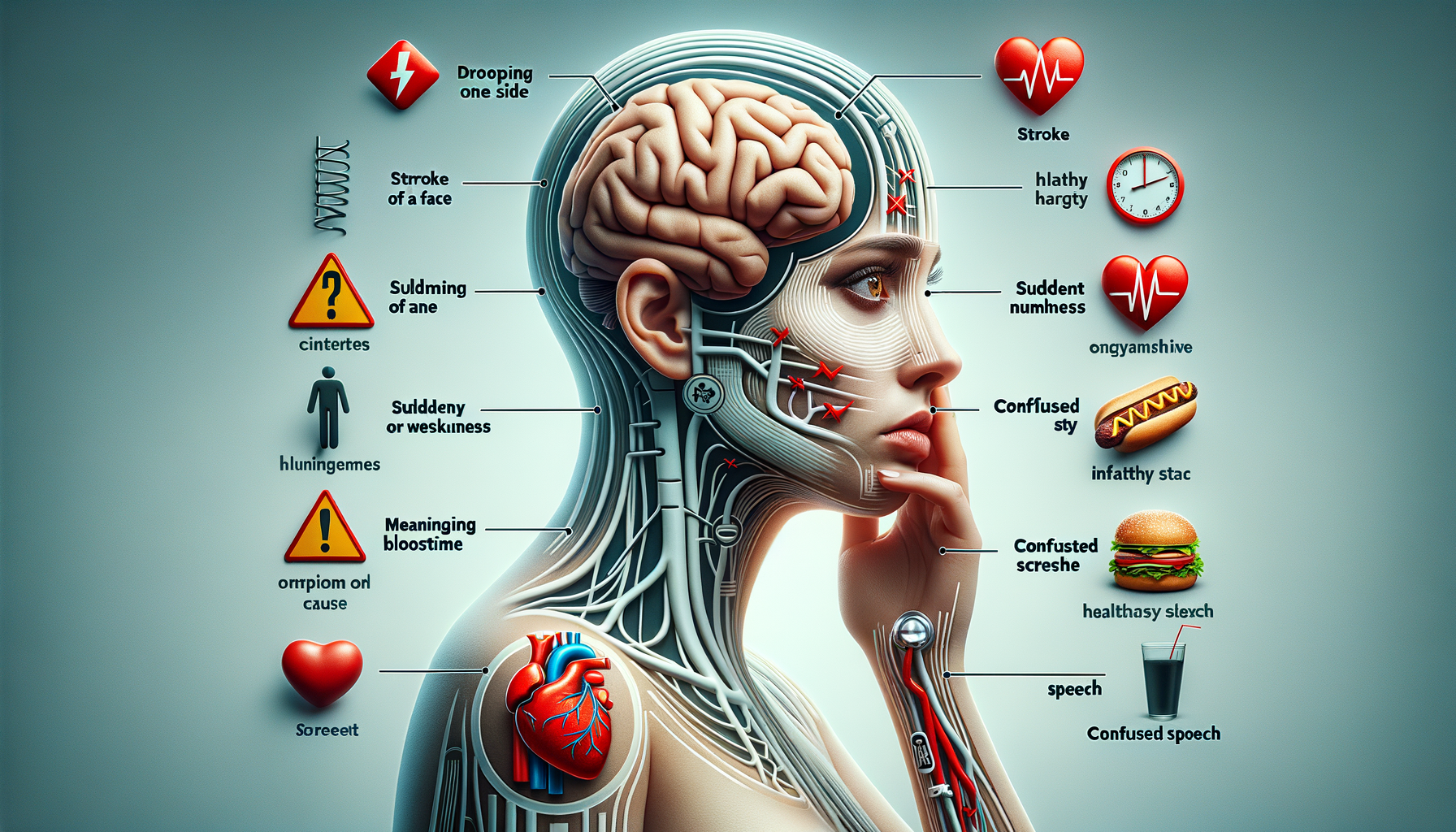
Common Symptoms of a Stroke
Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke is the first step in seeking timely medical intervention. The symptoms can vary depending on the type of stroke and the area of the brain affected. Common warning signs include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of balance and coordination.
- Severe headache with no known cause.
The acronym FAST can help remember the warning signs: Facial drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, and Time to call emergency services. Acting quickly by recognizing these symptoms can be crucial in reducing the impact of a stroke.
Types of Strokes and Their Causes
Strokes are broadly classified into two categories: ischemic and hemorrhagic. An ischemic stroke, accounting for about 87% of all cases, occurs when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery leading to the brain. This blockage can be due to fatty deposits lining the vessel walls or a clot that travels from another part of the body.
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding in or around the brain. This can result from conditions such as high blood pressure, aneurysms, or arteriovenous malformations. Understanding these types and their causes can help in both prevention and management strategies.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of having a stroke. Some are uncontrollable, such as age, family history, and previous stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). However, many risk factors can be managed or mitigated through lifestyle changes and medical intervention:
- High blood pressure: Regular monitoring and medication can help control blood pressure.
- Smoking: Quitting smoking reduces the risk of stroke significantly.
- Diabetes: Proper management of blood sugar levels is crucial.
- High cholesterol: Diet, exercise, and medication can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
- Physical inactivity and obesity: Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can lower stroke risk.
By addressing these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of stroke.
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness
Understanding the symptoms and causes of strokes is vital for prevention and effective response. Early recognition of warning signs can lead to timely medical intervention, significantly improving the chances of recovery. By managing risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Public awareness and education are key components in combating this serious health issue, ensuring that more people are equipped to act fast and seek help when necessary.



Leave a Reply